Machine learning
By Abhi Suresh,
5th Sem, Dept of EEE
An exciting branch of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning is all around us in this modern world. Like Facebook suggesting the stories in your feed, Machine Learning brings out the power of data in a new way. Working on the development of computer programs that can access data and perform tasks automatically through predictions and detections, Machine Learning enables computer systems to learn and improve from experience continuously.
As you feed the machine with more data, thus enabling the algorithms that cause it to “learn,” you improve on the delivered results. When you ask Alexa to play your favorite music station on the Amazon Echo, she will go to the one you have played the most; the station is made better by telling Alexa to skip a song, increase volume, and other various inputs. All of this occurring because of Machine Learning and the rapid advance of Artificial Intelligence.
How Does Machine Learning Work?
Machine Learning is, undoubtedly, one of the most exciting subsets of Artificial Intelligence. It completes the task of learning from data with specific inputs to the machine. It’s important to understand what makes Machine Learning work and, thus, how it can be used in the future.
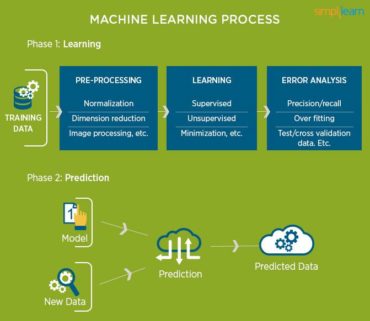
The Machine Learning process starts with inputting training data into the selected algorithm. Training data being known or unknown data to develop the final Machine Learning algorithm. The type of training data input does impact the algorithm, and that concept will be covered further momentarily.
To test whether this algorithm works correctly, new input data is fed into the Machine Learning algorithm. The prediction and results are then checked.
If the prediction is not as expected, the algorithm is re-trained multiple numbers of times until the desired output is found. This enables the Machine Learning algorithm to continually learn on its own and produce the most optimal answer that will gradually increase in accuracy over time.
Types of Machine Learning
Machine Learning is complex in itself, which is why it has been divided into two main areas, supervised learning and unsupervised learning. Each one has a specific purpose and action within Machine Learning, yielding particular results, and utilizing various forms of data. Approximately 70 percent of Machine Learning is supervised learning, while unsupervised learning ranges from 10 – 20 percent. Another method that is used less often is reinforcement learning.
Supervised Learning
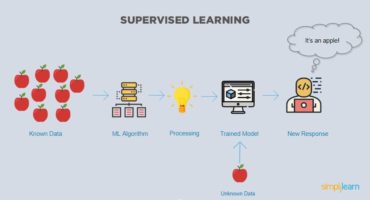
In supervised learning, we use known or labeled data for the training data. Since the data is known, the learning is, therefore, supervised, i.e., directed into successful execution. The input data goes through the Machine Learning algorithm and is used to train the model. Once the model is trained based on the known data, you can use unknown data into the model and get a new response.
In this case, the model tries to figure out whether the data is an apple or another fruit. Once the model has been trained well, it will identify that the data is an apple and give the desired response.
The top algorithms currently being used for supervised learning are:
- Polynomial regression
- Random forest
- Linear regression
- Logistic regression
- Decision trees
- K-nearest neighbors
- Naive Bayes
Unsupervised Learning
In unsupervised learning, the training data is unknown and unlabeled – meaning that no one has looked at the data before. Without the aspect of known data, the input cannot be guided to the algorithm, which is where the unsupervised term originates from. This data is fed to the Machine Learning algorithm and is used to train the model. The trained model tries to search for a pattern and give the desired response. In this case, it is often like the algorithm is trying to break code like the Enigma machine but without the human mind directly involved but rather a machine.
In this case, the unknown data consists of apples and pears which look similar to each other. The trained model tries to put them all together so that you get the same things in similar groups.
The top algorithms currently being used for unsupervised learning are:
- Partial least squares
- Fuzzy means
- Singular value decomposition
- K-means clustering
- Apriori
- Hierarchical clustering
- Principal component analysis
Reinforcement Learning
Like traditional types of data analysis, here, the algorithm discovers data through a process of trial and error and then decides what action results in higher rewards. Three major components make up reinforcement learning: the agent, the environment, and the actions. The agent is the learner or decision-maker, the environment includes everything that the agent interacts with, and the actions are what the agent does.
Reinforcement learning occurs when the agent chooses actions that maximize the expected reward over a given time. This is easiest to achieve when the agent is working within a sound policy framework.
Why Machine Learning?
To better understand the uses of Machine Learning, consider some instances where Machine Learning is applied: the self-driving Google car; cyber fraud detection; and, online recommendation engines from Facebook, Netflix, and Amazon. Machines can enable all of these things by filtering useful pieces of information and piecing them together based on patterns to get accurate results.
The process flow depicted here represents how Machine Learning works:
The rapid evolution in Machine Learning has caused a subsequent rise in the use cases, demands—and, the sheer importance of ML in modern life. Big Data has also become a well-used buzzword in the last few years. This is, in part, due to the increased sophistication of Machine Learning, which enables the analysis of large chunks of Big Data. Machine Learning has also changed the way data extraction and interpretation are done by automating generic methods/algorithms, thereby replacing traditional statistical techniques.
Uses of Machine Learning
Typical results from Machine Learning applications we either see or don’t regularly include web search results, real-time ads on web pages and mobile devices, email spam filtering, network intrusion detection, and pattern and image recognition. All these are by-products of using Machine Learning to analyze massive volumes of data.
Traditionally, data analysis was trial and error-based, an approach that becomes impossible when data sets are large and heterogeneous. Machine Learning provides smart alternatives to analyzing vast volumes of data. By developing fast and efficient algorithms and data-driven models for real-time processing of data, Machine Learning can produce accurate results and analysis.
According to a related report by McKinsey, “As ever more of the analog world gets digitized, our ability to learn from data by developing and testing algorithms will only become more important for what is now seen as traditional businesses.” The same report also quotes Google’s chief economist Hal Varian who calls this “computer kaizen” and adds, “just as mass production changed the way products were assembled, and continuous improvement changed how manufacturing was done… so continuous (and often automatic) experimentation will improve the way we optimize business processes in our organizations.” Machine Learning is here to stay.
Some Machine Learning Algorithms And Processes
If you’re studying Machine Learning, you should familiarize yourself with standard Machine Learning algorithms and processes. These include neural networks, decision trees, random forests, associations, and sequence discovery, gradient boosting and bagging, support vector machines, self-organizing maps, k-means clustering, Bayesian networks, Gaussian mixture models, and more.
To get the most value out of Big Data, other Machine Learning tools and processes that leverage various algorithms include:
- Comprehensive data quality and management
- GUIs for building models and process flows
- Interactive data exploration and visualization of model results
- Comparisons of different Machine Learning models to quickly identify the best one
- Automated ensemble model evaluation to determine the best performers
- Easy model deployment so you can get repeatable, reliable results quickly
- An integrated end-to-end platform for the automation of the data-to-decision process
Machine Learning Prerequisites
For those interested in learning more about breaking into the field of Machine Learning, a few requirements should be met to be successful in pursual of this field. These requirements include:
- Basic knowledge of programming and scripting languages
- Intermediate knowledge of statistics and probability
- Basic knowledge of linear algebra. In the linear regression model, a line is drawn through all the data points, and that line is used to compute new values.
- Understanding of calculus
- Knowledge of how to clean and structure raw data to the desired format to reduce the time taken for decision making.
Each of these prerequisites will help you quickly succeed in transitioning into Machine Learning. For a refresh on the various prerequisites above, the Simplilearn YouTube channel provides succinct and detailed overviews.
Conclusion
- Machine learning and other AI based system are disrupting many industries and bringing us smarter, more targeted products and services.
- Education and training are already feeling the way of these technologies and will be dramatically transformed by them.
- Data-driven adaptive training will become the industry standard as we move towards competency based training.
Machine Learning is the future. The future is now, are you ready to transform?