Inertial Measurement Units IMUs
The locations of vehicles such as drones, robots and self-driving cars, remote control ships etc. are determined by the sensors that is embedded into these vehicles. This operation occurs by calculating the acceleration, displacement and orientation of vehicles. There are many sensors do this operation like as shown below.
1. Accelerometer
it is an electromechanical device that sense static acceleration (gravity) and dynamic acceleration (vibrations & movement), its function is measuring the acceleration in one or more directions. Also, the position can be deduced by integrating the acceleration equation and orientation sensing by tilt sensor and vibration sensing. There are many types of accelerometer such as :
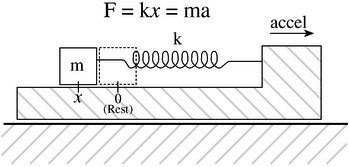
1.1. Mass spring accelerometer
It is an instrument that measures the rate at which the acceleration of an object is changing. The accelerometer measures the force exerted by restraints that are placed on a reference mass to hold its position fixed in an accelerating body. The acceleration is computed using the relationship between restraint force and acceleration given by Newton’s second law Force = mass x acceleration
1.2. MEMS accelerometer
MEMS is the shortcut of MicroElectroMechanical Systems. These techniques create mechanical sensing structures of microscopic size, typically based on silicon when coupled with microelectronic circuits. There are two types of MEMS accelerometers: variable capacitive and piezoresistive. Variable capacitive VC MEMS accelerometers have lower range and high sensitivity and used for structural monitoring in Buildings and constant acceleration measurements such as gravity. Piezoresistive (PR) MEMS accelerometers have higher range and low sensitivity and used in shock and blast applications.

Piezoresistive MEMS Accelerometer
Variable capacitive MEMS Accelerometers
2. Gyroscope
It is measures the orientation or angular velocity or the rate of rotation along 3-axes. Their are Pitch(X angle), Roll (Y angle) and Yaw (Z angle). It is used in automatic pilots on ships and aircraft, in the steering mechanisms of torpedoes, and in the inertial guidance systems installed in space launch vehicles, ballistic missiles, and orbiting satellites.

3. Compass
It is an instrument used for navigation and orientation that shows direction relative to the geographic cardinal directions . Digital or electronic Compass Sensor is actually a magnetometer that can measure the Earth’s magnetic field by use Hall Effect sensor and by calculating the very low frequency signals coming from the North or South direction, this sensor can calculate the orientation and direction. It is used in navigation systems, Localization and marine applications etc.
Hall Effect Sensor of Compass
4. Gyrocompass, it is similar to a gyroscope. But it is a non- magnetic compass that finds true north by using an (electrically powered) fast-spinning wheel and friction forces in order to exploit the rotation of the Earth. They have an advantage over magnetic compasses.They are not affected by ferromagnetic metal (iron, steel, cobalt, nickel,etc). However, magnetic compasses are still widely in use due to they can be small, use simple reliable technology, cheap, easier to use than GPS and they require no energy supply unlike GPS.Also they are not affected by objects such as the walls or big trees which block the reception of electronic signals.
5. Inertial Measurement Unit IMU
It is an electronic device which consists of a set of sensors like accelerometers, gyroscopes and magnetometers. It is measures a force, angular rate and orientation of the object. The IMU detect acceleration using accelerometers, heading reference by using magnetometer and the orientation by using gyroscopes. Each axis of the three object axes (pitch, roll, yaw) contain one accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer.
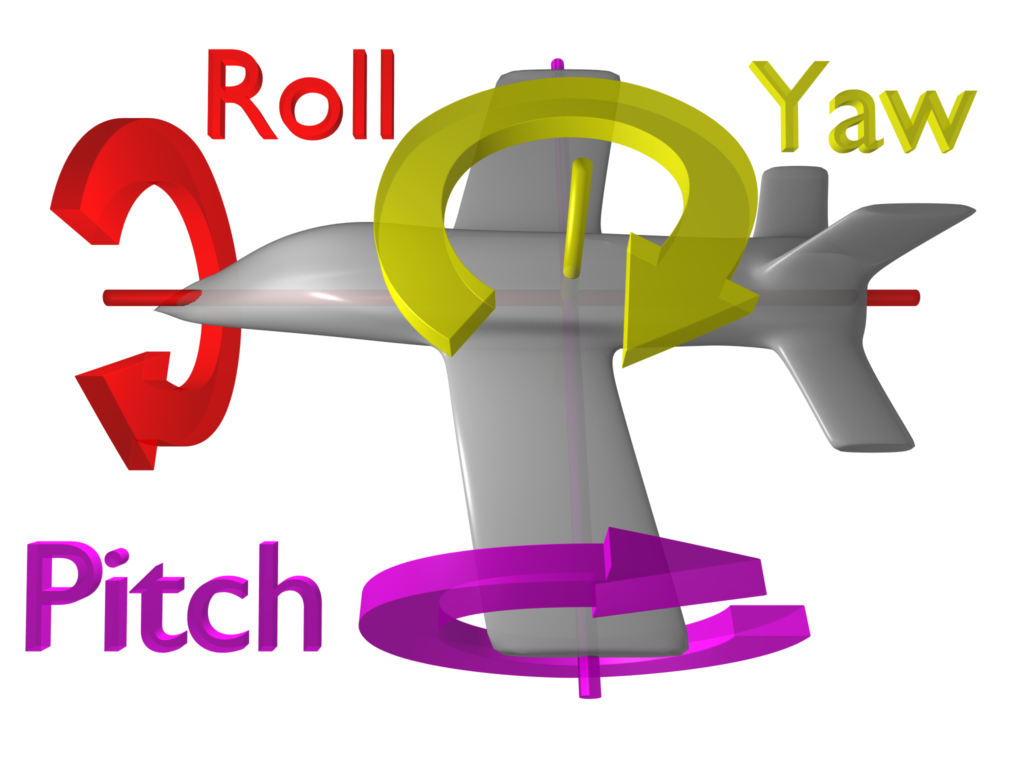
6. Attitude and Heading Reference System AHRS, it is a type of 3-axes inertial measurements units. Also, it is an electronic device which has a set of sensors like MEMS gyroscopes, accelerometers, magnetometers and on-board processor. It can measure a heading (yaw), pitch and roll angles of any object moving in space.
The main difference between of IMU and AHRS that is, the AHRS has a data processing unit (on-board processor) in the same device. So, AHRS capable for fusioning the data from various sensors and determine the attitude and heading information of the moving object in the same device. So, we can say that AHRS is real time orientation tracking. Also an on-board Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) handles the tricky data fusion problem and estimate the future measurements for both accelerometers and gyroscopes. But IMU not capable for processing the data in the same device but it transmits the sensor’s data to another device to determine the attitude and heading information.

Application on Positioning
» Article Citation
Written by Israa, A . (2020, June 18). Positioning Sensors, IEEE AIET SB. Retrieved from https://edu.ieee.org/eg-aiet/positioning-sensors/
» References
[1] https://www.pcb.com/resources/technical-information/mems-accelerometersfbclid=IwAR22y05Y_TZN3MQgRIiX5xIjUARXTspjjS5uD9HpiRQKItftVnx_6KVJHZE
[6] https://www.sennavs.com/ahrs-vs-imu/
[7] https://www.vectornav.com/support/library/ahrs


Leave A Comment